SMEs are Small and Medium Enterprises
defined by Government by their revenue. In India the Government has defined
businesses with revenue upto INR 50 million as a micro enterprise, those with sales
between INR 50 million and INR 75 million will be deemed as small and those with revenue
between INR 750 million and INR 250 million will be classified as medium-sized
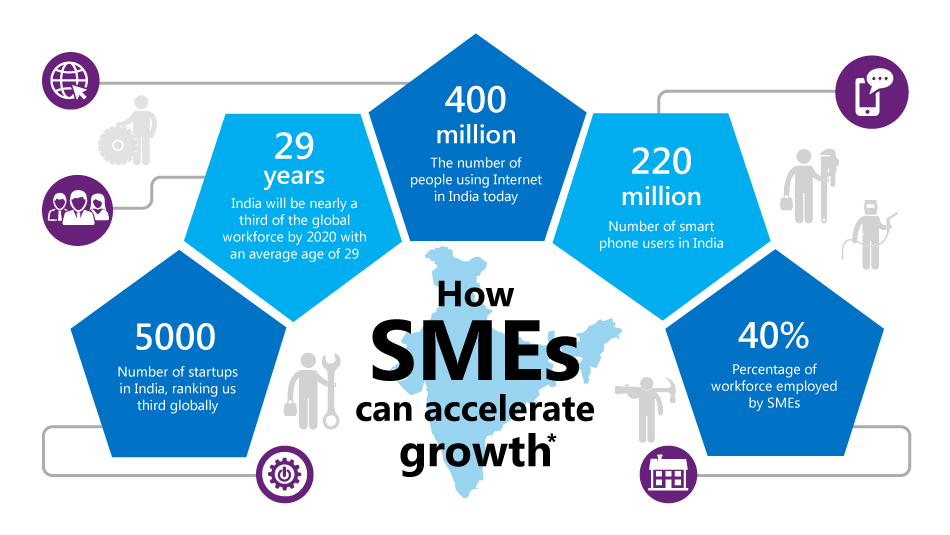
enterprises. It is well accepted fact that SMEs play a key role in driving
overall growth of economy. SMEs are drivers of economic growth and job creation
in developing countries.
They face challenges in terms of
capital expenditure, labor and other different issues. Here in this article, we
have tried to identify the key factors that help SMEs to grow?
Management Practices:
In any business, growth is not
linear. Therefore management practices play a crucial role in ensuring the
growth of the business. The business is successful only when there is a high
degree of operational and management efficiency that leads to higher
productivity. Therefore the management strategy should fit to the core business
of the company and be ready to adapt change quickly.
The key areas that have been
identified for improving management practices are internal controls, labor
benefits, strategic planning that includes fund raising and innovation. If
these areas are managed well then the company can scale up faster that the
market. They should have feasibility studies conducted for the business and dynamically update the data as required.
Talent Management: Employees are of great importance in
ensuring growth of a business. Businesses become successful when they align
staff performance to wider business targets. This helps in augmenting the
process of achieving short term and long term goals.
In that context, it is worthy to
mention that, not only productivity of staffs but also their behavior must be
aligned with overall organizational goal. Teams and employees are able to achieve
monthly goals set when they are motivated, compensated adequately and there is a
desire to achieve the broader organizational goals. Some of the key factors
that we have identified for talent management are:
It is understandable that for SMEs
there is not much space to promote employees. Therefore they can be delegated
greater responsibility so that it sums up to more of a horizontal promotion for
them. Create physical or online groups in the office so that they can get
involved in some activity on a Friday.
There can be several such activities
but the broader point that needs to be reflected is how employees can be kept
motivated at all times.
Adoption of Technology:
If we are not technologically up to
date we will suffer as we’re going through a digital revolution. The companies that
failed to make themselves technology intensive have disappeared from the
market. Technology can be costly in initial stages of the business. But, it
gives considerable competitive advantage by reducing cost of productivity and
enhancing quality of productivity.
It is difficult for SMEs to install
robotics in its operations. Dedicated industrial robots can limit small and
mid-sized manufacturers who often have small production batches and require
fast change-over. But, these issues are solved by innovative Universal Robot.
It is easy to install and reprogram, less spacious and redeployable in multiple
locations. Thus, using this technology SMEs which are operating in the
manufacturing industry can achieve economies of scale which contributes
positively in achieving growth in the business.
Based upon my experience of working
with the SME sector, I have seen that some SMEs are moving towards
implementing better technology. For example a SME Agri Implement Manufacturer
can use powder coated painting for the products which is parallel to what large
manufacturers do.
R&D and Innovation:
It is known that R&D and
innovation are key reasons for growth of a business. Without it a business,
product and service become cliché and ineffective. TR&D and innovation has
made Apple Inc. and Google distinct from other companies. But, all the SMEs do
not have the capacity to invest in R&D. However, if it fails to innovate,
it fails to achieve growth.
However, SMEs are, on average, less
innovative than large companies. For example, across OECD countries, the median
value in the national SME share of business R&D is 35%. That is why it
takes time for many SMEs to achieve high growth in initial stages of the
business.
India spends around 0.8% of its GDP
in R&D. Government, business and universities are the key sectors where it
spends on R&D. In 2018, it spent $29,066.8 million in government sector, $17,044.0 million in business sector and $1,952.3 million in universities. However, there are no defined
figures of how much is being spent on SME R&D. Thus, investing in R&D and
innovation in SMEs is still not considered high priority.
Networks and External Engagement:
The key notion of business is selling
products and services and earning revenue. Therefore, the businesses which have
better network and external engagement are able to generate revenue easily. It
allows these SMEs to develop better engagement with existing clients to enhance
the expansion of the present client base easily which results in a consistent
growth from early stages of business.
Most of the SMEs focus on listing their
business in various classified sites, participate in forums, post blogs,
conduct events and forge partnership for enhanced networking and better external
engagement to ensure growth of business. In India SMEs participate in various
events conducted by NASSCOM, ASSOCHAM and other to expand their clients base.
Online promotions that include Social Media and Google advertisements are also
becoming a key channel to promote SME business.
Access to Funding:
High-growth SMEs are not just more
likely to seek external funding but also a broader range of funding options to
suit their scale-up needs. The companies build an external funding network. It
helps to diversify funding sources and reduces the risk of investment. However,
many low-growth SMEs misses out on this opportunity due to various reasons such
as not-so-attractive business idea, restricted scope of generating revenue and inability
to refund on time.
That is why formal banking system refrains
from investing in small and medium sized businesses. An analysis conducted by
IFC revealed that, there is an approximate amount of $240 billion credit gap in
India. In India, micro, small and medium enterprises are responsible for around
30% of economic output and it provides employment to around 111 million people.
However, the growth in Fintech industry in India shows a new hope for SMEs to
access required funds for its businesses. According to PwC report, Indian and
global venture capital investors are more inclined to invest in this segment.
Governmental policies: India is expected to be a $5 trillion
economy by 2025. The country was recently termed as truly emerging market in
Asia at the moment. In 2019, the SMEs have been identified with 60% increased
in offering app-based services. Thus, they are increasingly becoming technology
intensive. However, this was impossible to happen ten years back. The budget
crunch and lack of business scope were played as key reasons. Various positive
government initiatives played key roles to enhance confidence among
entrepreneurs to invest in their startup.
Key government policies that has
helped SMEs to startup are MSME business loans in 59 minutes, MUDRA
(Micro-Units Development and Refinance Agency), CGMSE (Credit Guarantee for
Micro and Small Enterprises) loan, NSIC (National Small Industries Corporation)
loan and CLCSS (Credit Link Capital Subsidy Scheme).
These funding schemes and loans have
enabled SMEs to overcome the problems faced by credit gaps in the industry. In
it worth to mention that MUDRA scheme helped many micro enterprises to avail
funding help of INR 50,000 while it enables to access loan upto INR 10 lakhs.
Therefore, these diverse financial
facilities catering to unique need of micro, small and medium sized enterprises
helped the SME segment to become as the futile seed of manifold growth of
economy within next few years.
In a concluding note it is worth
mentioning that SMEs are the backbone of Indian economy. The report published
by Goldman Sachs says small businesses are the engines of job creation in
America. It accounts for 29.6 million businesses in America. It comprises 99%
of US employment firms. It employs around 58 million people in America.
According the statistics provided by Federation of Small Business of UK, Small
businesses accounted for 99.3% of all private sector businesses at the start of
2018 and 99.9% were small or medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Therefore, due to
the positive impact of various initiatives and existent external and internal
drives, India is steadfastly moving towards a right direction by ensuring scope
of growth across SMEs.

COMMENT(S)
LEAVE A REPLY